Broad Tailed Hummingbird Migration Map: Explore!
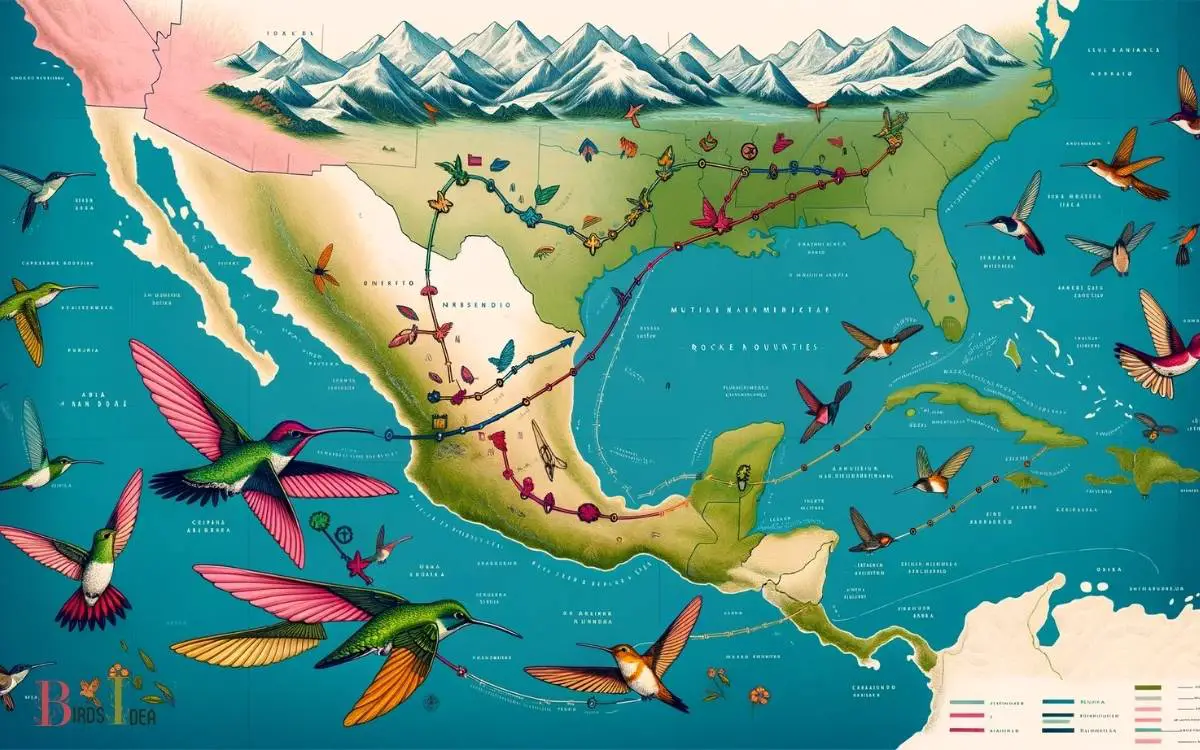
The Broad-tailed Hummingbird Migration Map is a crucial resource that illustrates the migratory paths taken by Broad-tailed Hummingbirds.
It highlights the seasonal movements from their breeding grounds, primarily located in the mountainous regions of the western United States, to their winter habitats in Central America.
This interactive tool helps birdwatchers, researchers, and conservationists track the annual journeys of these birds and understand the timing and geography of their migration.
The map outlines the routes based on observations and tracking data, indicating:
The use of GPS technology, banding information, and contributions from citizen scientists provides a detailed picture of the Broad-tailed Hummingbird’s migration.
Discover the fascinating voyage of Broad-tailed Hummingbirds through detailed migratory maps.
Key Takeaway
4 Location for Broad-Tailed Hummingbird Migration
| Location | Arrival Timeframe | Departure Timeframe | Notable Migration Observations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mexico | Early March | Late October | Wintering grounds for many hummingbirds; migration begins here |
| Southern US | Mid-March | Early October | First US stops on migration; breeding grounds for some |
| Central US | Late March | Late September | Breeding grounds; rich with flowering plants for feeding |
| Northern US | Early April | Mid-September | Final US destination before returning south; breeding and feeding |
Understanding Hummingbird Migration
Understanding Hummingbird Migration involves studying their behaviors and patterns during different seasons. These tiny birds undertake remarkable long-distance journeys, with some species traveling up to 3,000 miles from their breeding grounds to their wintering grounds.
The study of hummingbird migration includes observing their feeding and roosting habits, the timing of their departure and arrival, and the routes they take.
Scientists use a variety of methods to track their movements, including banding, radio telemetry, and citizen science initiatives.
By understanding the intricacies of hummingbird migration, researchers can gain insights into the factors driving these migrations, the impact of environmental changes, and the conservation of critical stopover sites.
This knowledge is vital for the development of effective conservation strategies and the preservation of these incredible migratory journeys.
Importance of Migration Mapping
Migration mapping of hummingbirds is essential for tracking their movements and understanding their migration routes and stopover sites.
- It allows researchers to unravel the mysteries of hummingbird migration, providing valuable insights into their behavior and ecology.
- Understanding their migration patterns can evoke a sense of wonder and appreciation for the incredible journeys these tiny birds undertake.
- By mapping their routes, we can also identify critical habitats and areas for conservation, invoking a sense of urgency and responsibility to protect these fragile ecosystems.
- Additionally, migration mapping helps in predicting and mitigating potential threats to hummingbirds, fostering a sense of empathy and a call to action to safeguard these remarkable avian travelers.
Accurate mapping is crucial for the conservation and management of these enchanting birds, thereby highlighting the significance of this scientific endeavor.
Key Migration Routes
The key migration routes of the Broad Tailed Hummingbird encompass major migration corridors, long-distance flight patterns, and the diverse habitats encountered along these routes.
Understanding these routes is crucial for conserving the species and its habitats, as well as for predicting and mitigating potential human-wildlife conflicts.
By examining the points of these routes, researchers can gain insights into the ecological and environmental factors that influence the hummingbird’s migration behavior.
Major Migration Corridors
During the spring and fall, broad-tailed hummingbirds migrate along key corridors throughout North America. These major migration corridors serve as vital pathways for the hummingbirds as they journey to their breeding and wintering grounds.
The awe-inspiring spectacle of thousands of tiny hummingbirds navigating these corridors evokes a sense of wonder and appreciation for the resilience of these remarkable creatures.
As they traverse these corridors, they encounter various challenges, including adverse weather conditions and the need for sufficient food sources to fuel their long journey.
Witnessing their determination and perseverance along these migration routes evokes a deep sense of admiration for the incredible feats these birds accomplish.
Understanding these major migration corridors is crucial for conservation efforts and ensuring the well-being of these fascinating creatures.
Long-Distance Flight Patterns
As they embark on their long-distance journey, broad-tailed hummingbirds follow key migration routes that are crucial for their seasonal movements.
These tiny birds undertake remarkable migrations, traveling thousands of miles between their breeding and wintering grounds.
The primary migration route for broad-tailed hummingbirds spans from their breeding grounds in western North America, including the United States and Canada, to their wintering grounds in Mexico and Central America.
Along this route, they navigate diverse landscapes, including mountain ranges, deserts, and tropical forests. The birds strategically utilize favorable wind patterns and nectar-rich stopover sites to refuel during their arduous journey.
Understanding these key migration routes is essential for conservation efforts and ensuring the protection of crucial habitats for the broad-tailed hummingbird’s survival.
Habitat Along Routes
Migration routes for broad-tailed hummingbirds are characterized by diverse habitats that play a crucial role in their seasonal movements.
These habitats evoke a sense of wonder and appreciation as the hummingbirds traverse through them, experiencing the beauty and challenges of the natural world.
The varied landscapes along their routes include:
- Lush, blooming meadows that provide abundant nectar sources for refueling.
- Dense, verdant forests offering shelter and protection from predators.
- Pristine, glistening lakes and rivers where the hummingbirds can quench their thirst and bathe in the cool waters.
These diverse habitats not only provide essential resources for the hummingbirds but also create a captivating backdrop for their awe-inspiring journey.
As the hummingbirds navigate through these habitats, they encounter a myriad of ecological wonders, shaping their remarkable migration. This sets the stage for understanding the seasonal variation in migration, which will be explored next.
Seasonal Variation in Migration
One significant aspect of the broad-tailed hummingbird migration is the seasonal variation in their movement patterns.
During the spring and summer, these tiny birds migrate from their wintering grounds in Mexico and Central America to their breeding grounds in the western United States.
As the days grow longer and the temperatures rise, the broad-tailed hummingbirds follow the blooming of flowers, their primary food source, northward.
In the fall, they make the return journey south, following the availability of nectar-rich flowers as they move to their wintering grounds. This seasonal variation in migration is driven by the hummingbirds’ reliance on floral resources for their survival.
Understanding these movement patterns is crucial for conservation efforts and managing habitats to support their migration.
Factors Affecting Migration Patterns
The migration patterns of broad-tailed hummingbirds are influenced by a variety of factors, including climate, food availability, and habitat suitability. These factors play a crucial role in shaping the routes and timing of their migration.
- Climate: The fluctuating temperatures and weather patterns impact the availability of nectar-producing flowers, affecting the hummingbirds’ food sources.
- Food Availability: The abundance of nectar-rich flowers along their migratory routes is a key determinant in the birds’ ability to refuel during their long journey.
- Habitat Suitability: The presence of suitable nesting sites and resting areas in different locations along their migration path is essential for the hummingbirds’ survival.
Understanding the influence of these factors provides valuable insights into the conservation and management of broad-tailed hummingbird populations.
Conservation Implications
An analysis of the broad-tailed hummingbird migration map reveals significant conservation implications for their habitat and population management. The map highlights critical stopover sites and breeding grounds essential for the species’ survival.
Conservation efforts should focus on preserving these key areas, ensuring they remain undisturbed and abundant in nectar-rich flowers.
Additionally, the map indicates potential threats along the migratory route, such as habitat loss and climate change impacts. Conservationists should address these threats by implementing measures to protect and restore vital habitats.
Furthermore, the map provides insights into the hummingbirds’ migratory pathways, aiding in the identification of areas requiring international collaboration for conservation efforts.
Understanding the migration map is crucial for developing effective conservation strategies to safeguard the broad-tailed hummingbird population for future generations.
Technology Behind Migration Tracking
Using advanced telemetry and GPS technology, researchers have been able to track the precise migratory routes of broad-tailed hummingbirds. This has provided invaluable insights into their behavior and habitat utilization.
The technology has allowed scientists to gather data on the exact timing and duration of their migration, as well as the specific stopover sites crucial for refueling.
This level of detail has deepened our understanding of the challenges these tiny birds face during their arduous journey, evoking a sense of empathy for the obstacles they encounter.
The use of cutting-edge technology has also fostered a profound appreciation for the complexity and beauty of avian migration, igniting a sense of wonder and awe in those who study these remarkable creatures
Citizen Science and Migration Data
Engaging citizen scientists in the collection of migration data has significantly impacted the field of migration research.
The involvement of volunteers in data collection has expanded the geographic scope of research, allowing for a more comprehensive understanding of migration patterns.
Citizen science initiatives have also facilitated the collection of long-term data, enabling researchers to track trends and changes in migration behavior over time.
Engaging Citizen Scientists
Citizen scientists play a crucial role in collecting migration data for the Broad Tailed Hummingbird Migration Map.
Engaging these volunteers fosters a sense of community and shared responsibility, as they contribute to a deeper understanding of these fascinating birds.
It also provides an opportunity for individuals to connect with nature on a profound level, fostering a sense of wonder and appreciation for the natural world.
Moreover, engaging in citizen science initiatives can evoke a sense of accomplishment and pride, as participants contribute meaningfully to ongoing research and conservation efforts.
Additionally, it can spark a sense of curiosity and a desire to learn more about the intricate behaviors and patterns of these birds, further enriching the experience for citizen scientists.
Impact on Migration Research
The involvement of volunteers in collecting migration data for the Broad Tailed Hummingbird Migration Map has significantly impacted migration research.
Citizen science initiatives have provided a wealth of data that would have been difficult to obtain through traditional research methods.
This large-scale data collection has allowed for a more comprehensive understanding of broad-tailed hummingbird migration patterns, including the identification of stopover sites, migration routes, and timing.
By engaging citizen scientists, researchers have been able to gather data from a wider geographic area, leading to a more holistic view of hummingbird migration.
Furthermore, the involvement of volunteers has sparked public interest and awareness in avian migration, fostering a community of individuals passionate about contributing to scientific research.
This collaborative approach has enhanced the depth and accuracy of migration data, providing valuable insights for conservation efforts and ecological studies.
Future of Hummingbird Migration Research
Moving forward, the focus of hummingbird migration research will be on understanding the impact of climate change on their migration patterns and behavior.
- This research will evoke concern as climate change could disrupt the availability of nectar-producing flowers crucial for hummingbird survival.
- The potential implications of disrupted migration patterns may evoke fear and uncertainty about the future of these magnificent birds.
- Understanding the effects of climate change on hummingbird migration will evoke a sense of urgency to take action in preserving their habitats.
This research aims to provide valuable insights into the ways in which climate change may be altering the traditional migratory routes of hummingbirds and the potential consequences for their survival.
Conclusion
The broad tailed hummingbird migration map provides valuable insights into the complex and fascinating phenomenon of hummingbird migration.
By tracking their key migration routes, seasonal variations, and the factors affecting their patterns, we can better understand and ultimately conserve these remarkable birds.
The future of hummingbird migration research holds great promise, especially with the advancement of technology and the contributions of citizen science in collecting valuable migration data.






