Do Hummingbird Moths Eat From Hummingbird Feeders?
Have you ever wondered if hummingbird moths partake from hummingbird feeders? Well, wonder no more!
These fascinating creatures, often mistaken for hummingbirds, exhibit a behavior that might surprise you.
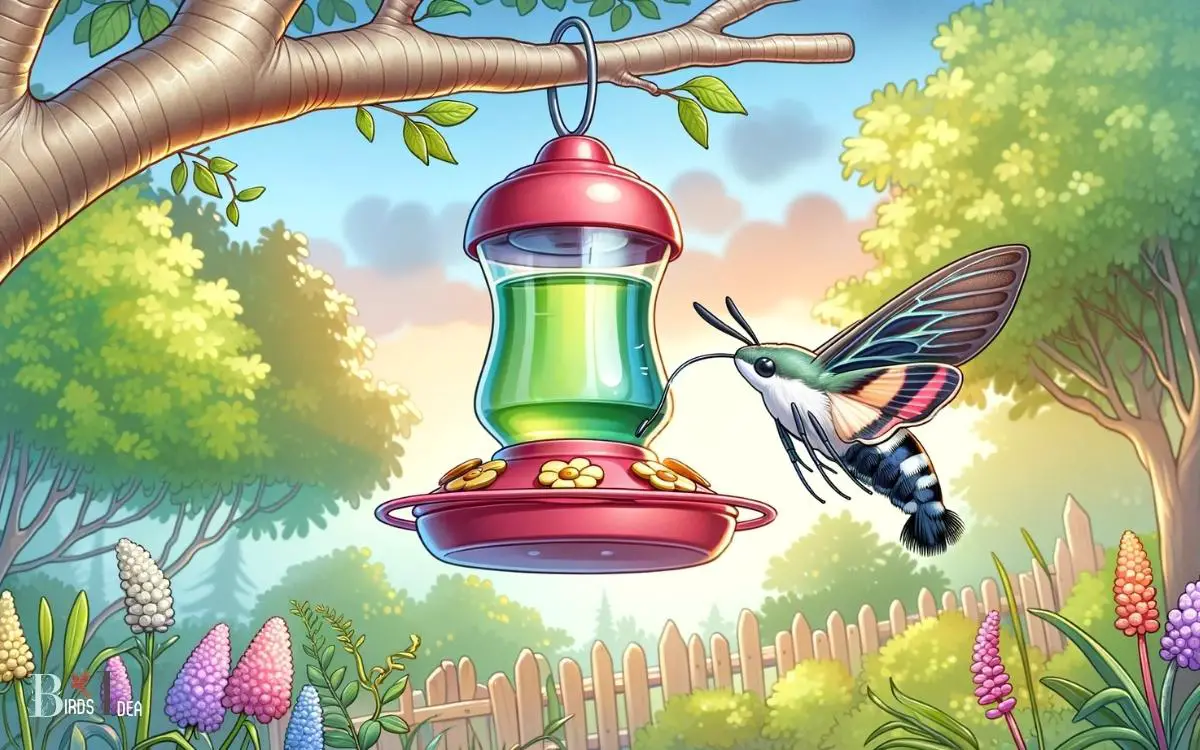
While often seen hovering near flowers to sip nectar, hummingbird moths do not typically feed from hummingbird feeders.
Understanding their feeding preferences and behaviors can help create an environment that attracts them to your garden.
With a few adjustments, you can enjoy the delightful presence of these enchanting insects as they flutter among your flowers, adding a touch of wonder to your outdoor space.
Let’s explore the intriguing world of hummingbird moths and uncover the secrets of their feeding habits.

Key Takeaway
Understanding Hummingbird Moth Behavior
Hummingbird moths exhibit diurnal feeding behavior similar to hummingbirds, actively seeking out nectar sources during daylight hours.
These moths, scientifically known as Hemaris, are often mistaken for hummingbirds due to their similar feeding patterns.
They prefer tubular, fragrant flowers such as honeysuckle, phlox, and verbena. Their long proboscis allows them to hover in front of flowers while they unfurl it to reach the nectar deep within.
Interestingly, their flight patterns also resemble those of hummingbirds, moving rapidly and erratically from flower to flower.
Observing them closely, one can notice their rapid wingbeats and their ability to hover in mid-air, much like their avian counterparts.
Understanding these behavioral traits is crucial in appreciating the ecological roles that hummingbird moths play in pollination and their unique adaptations for survival.
Nectar Sources for Hummingbird Moths
The diurnal feeding behavior of hummingbird moths leads them to seek nectar from a variety of tubular, fragrant flowers, including honeysuckle, phlox, and verbena.
Honeysuckle
- Honeysuckle’s long, tubular flowers provide ample nectar for hummingbird moths.
- The sweet fragrance and vibrant colors of honeysuckle attract these moths during daylight hours.
Phlox
- Phlox flowers offer a rich source of nectar, making them a favored feeding spot for hummingbird moths.
- The clustered, tubular blooms of phlox are well-suited for the moths’ feeding mechanism.
Verbena
- Verbena’s compact clusters of small, tubular flowers are highly attractive to hummingbird moths.
- The prolific nectar production of verbena flowers ensures a valuable food source for these fascinating insects.
Attracting Hummingbird Moths to Your Garden
To attract hummingbird moths to your garden, plant a variety of tubular, fragrant flowers such as honeysuckle, phlox, and verbena.
These flowers provide the nectar that hummingbird moths seek. Additionally, consider including evening primrose, petunias, and salvia, as these also attract these fascinating creatures.
Hummingbird moths are particularly drawn to white, pink, and purple flowers, so incorporating these colors into your garden can increase the likelihood of their presence.
It’s important to plant these flowers in clusters to create a concentrated food source that will catch the attention of hummingbird moths.
By providing an environment rich in nectar-producing flowers, you can effectively attract these delightful insects to your garden.
Differentiating hummingbird moths from hummingbirds can be challenging due to their similar appearance, but there are key distinctions.
Differentiating Hummingbird Moths From Hummingbirds
Most gardeners struggle to distinguish between hummingbird moths and hummingbirds due to their similar appearance.
This confusion is understandable as both species exhibit rapid wing movements and are attracted to similar flowers.
To differentiate between them, consider the following:
Physical Characteristics
- Hummingbird moths have stout, furry bodies and long, narrow wings, while hummingbirds have slender bodies and shorter, broader wings.
- Hummingbird moths often have clear or transparent wings with distinct black markings, while hummingbirds have opaque, iridescent wings.
Behavioral Cues
- Hummingbird moths are primarily active during dawn and dusk, while hummingbirds are active throughout the day.
- Hummingbird moths produce a distinct buzzing sound while in flight, whereas hummingbirds are relatively silent.
Feeding Patterns
- Hummingbird moths use their long proboscis to feed on nectar from flowers, while hummingbirds use their beaks to sip nectar and consume small insects.
Can Hummingbird Moths Compete with Hummingbirds for Food Sources?
Yes, hummingbird moth feeding habits can indeed compete with those of hummingbirds for food sources. Hummingbird moths have long tongues, similar to those of hummingbirds, allowing them to feed on the same nectar-producing flowers. This competition for resources can affect both species’ access to food.
Tips for Observing Hummingbird Moths
Observing hummingbird moths requires patience and attentiveness to their preferred feeding and resting areas.
These fascinating creatures are most active during the early morning and late afternoon when they visit flowers for nectar.
To increase the chances of observing hummingbird moths, one should seek out gardens with an abundance of their favorite nectar-producing plants, such as bee balm, phlox, and honeysuckle.
Additionally, creating a welcoming environment by planting these flowers in clusters can attract more moths.
Observers should also note that hummingbird moths are particularly drawn to tubular-shaped flowers.
When attempting to observe these moths, it is essential to move slowly and avoid sudden movements to prevent startling them.
The table below provides a list of plants that attract hummingbird moths.
| Plants | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Bee Balm | Rich nectar source, vibrant blooms |
| Phlox | Sweet fragrance, attracts moths and butterflies |
| Honeysuckle | Abundant nectar, long-blooming |
| Lilac | Fragrant blossoms, attracts pollinators |
Conclusion
While hummingbird moths may resemble hummingbirds in their feeding behavior, they’re in fact different species with distinct dietary preferences.
By understanding their behavior and providing the right nectar sources, gardeners can attract these fascinating creatures to their gardens.
Observing the delicate dance of a hummingbird moth as it flits from flower to flower is like witnessing nature’s own ballet, a graceful performance that adds beauty and wonder to the natural world.