What Color Is a Hummingbird Egg: White or Off-White!
Hummingbird eggs are typically white or off-white in color.
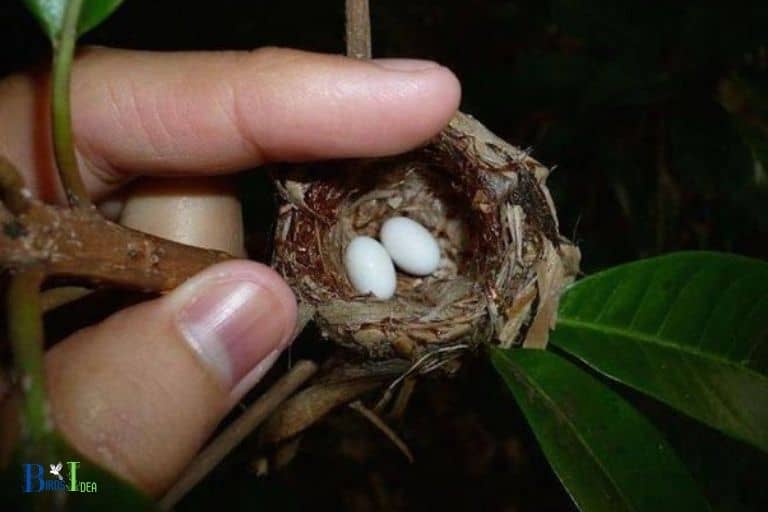
Hummingbirds lay small, oval-shaped eggs that are generally pearly white in color.
The size of these eggs is roughly equivalent to a small jelly bean or a large pea, making them one of the smallest bird eggs.
The egg’s color is meant to blend in with the surroundings, aiding in camouflage and protection from predators.
Hummingbird eggs are approximately the size of a jellybean and the speckled pattern helps to protect the egg from predators.
The eggs are generally laid one at a time and both parents will work together to incubate the eggs and care for the hatchlings.
11 Species About the Color of Hummingbird Eggs
| Hummingbird Species | Egg Color |
| Ruby-throated Hummingbird | White |
| Black-chinned Hummingbird | White |
| Anna’s Hummingbird | White |
| Costa’s Hummingbird | White |
| Rufous Hummingbird | White |
| Calliope Hummingbird | White |
| Broad-tailed Hummingbird | White |
| Violet-crowned Hummingbird | White |
| Allen’s Hummingbird | White |
| Blue-throated Mountain Gem | White |
| Note: The egg color of most hummingbird species is white. |
Key Takeaway

Five Facts About: Hummingbird Eggs
DID YOU KNOW
Hummingbird eggs are on average the size of a jellybean and both their parents help to incubate them until they hatch.
How Are Hummingbird Eggs Classified?
Hummingbird eggs are classified into two types: white eggs and blue eggs.
White eggs are laid by most hummingbird species and are typically oval in shape. They are often speckled with brown, gray, or black spots and can be as small as 0.5 inches in length.
White eggs usually have a smooth texture and are quite fragile. Blue eggs are laid by very few hummingbird species.

They are rounder in shape than white eggs and are usually a vivid blue-green color. Blue eggs tend to be slightly larger than white eggs and their texture is more coarse.
Hummingbird eggs are laid in nests made from plant fibers, downy feathers, and spider web silk. The female lays two eggs in each nest, which hatch after about two weeks.
The female will take care of the chicks until they are ready to leave the nest and start foraging for food on their own.
Hatchlings rely on their parents to provide warmth and protection until they can fly on their own.
birdsidea
What Color Are Hummingbird Eggs?
Hummingbird eggs are usually white in color. Depending on the type of hummingbird, the eggs may range in color from light blue to a deep blue-green color.
On average, hummingbird eggs are about the size of a small jellybean or a large pea.
Hummingbird eggs are laid singly in a nest, which is typically cup-shaped and made from spider webs, moss, lichen, and plant down.

The female hummingbird lays two eggs and incubates them for about two weeks until they hatch. During this time, the male hummingbird will feed the female.
For example, Anna’s hummingbird eggs are creamy white and speckled with reddish-brown spots. When they are first laid, they are slightly glossy but they will dull in color as they age.
The male Anna’s hummingbird will feed the female while she incubates the eggs, which helps the female stay warm and conserve energy.
The Role Of Camouflage In Egg Coloration
Hummingbird eggs come in a variety of colors, and one of the main reasons for this is their role in camouflage.
The coloration of the eggs helps protect them against predators, allowing them to blend seamlessly into their surroundings.
Let’s explore how egg coloration helps these tiny eggs stay hidden from harm’s way.
How Egg Color Helps Protect Against Predators
Egg color plays a crucial role in protecting hummingbird eggs from predators.
Here are some key points to understand this fascinating adaptation:
- Camouflage: The color of hummingbird eggs allows them to blend in with their environment, making it difficult for predators to detect them.
- Disguise: Certain hummingbird species lay eggs that are similar in color to their surroundings, whether it be the nest lining, vegetation, or tree bark.
- Predator confusion: The diverse range of egg colors in different hummingbird species can create confusion for predators.
- Dependence on habitat: Hummingbirds often build their nests in specific habitats, such as trees or shrubs, where the coloration of the eggs ensures they blend seamlessly into the natural environment.
Examples Of Effective Camouflage Strategies
Hummingbird eggs employ various camouflage strategies to protect themselves from predators.
Here are some notable examples:
- Cryptic coloration: Some hummingbird eggs have a cryptic coloration, allowing them to closely mimic their surroundings.
- Pattern camouflage: Certain hummingbird species lay eggs with intricate patterns that resemble the dappled light and shadow found in their nesting habitat.
- Background matching: Birds like the ruby-throated hummingbird lay eggs with a light blue or greenish-blue color that perfectly matches the color of the sky when viewed from below.
The coloration of hummingbird eggs serves as an essential defense mechanism against predators.
Their ability to blend in with their environment through camouflage ensures the eggs remain hidden and increases their chances of surviving until they hatch.
This remarkable adaptation is just one of the many awe-inspiring aspects of these tiny, yet resilient creatures.
Keep exploring to learn more about the fascinating world of hummingbirds and their incredible survival strategies.
Interesting Facts About Hummingbird Eggs
Hummingbird eggs are fascinating creations of nature, and they possess some unique features that distinguish them from other bird eggs.
Size And Shape Variations
- Hummingbird eggs vary in size. While some species lay eggs that are as small as a pea or a jellybean, others produce slightly larger eggs that can be compared to a small grape or even a marble.
- These tiny eggs often have elongated shapes, resembling miniature footballs. The pointed ends aid in preventing them from rolling off the nest during incubation.
Number Of Eggs Per Clutch
- Hummingbirds typically lay exceptional small clutches of eggs compared to other birds. A typical clutch size for hummingbirds ranges from just one to three eggs. The number varies depending on the species and environmental conditions.
- Some species, such as the anna’s hummingbird, tend to lay larger clutches with three eggs being the norm, while others like the ruby-throated hummingbird usually lay only one or two eggs.
Incubation Periods And Parental Care
- Once the female hummingbird has laid her eggs, she takes on the primary responsibility of incubation. The incubation period for hummingbird eggs usually lasts from 14 to 23 days, again varying by species.
- During this time, the female meticulously tends to her eggs, keeping them warm and protecting them from potential threats. She sits on the nest for long durations, only taking short breaks for feeding.
- After hatching, the female continues to care for the hatchlings, providing them with warmth and nourishment. The mother hummingbird feeds her young ones a specialized diet consisting of nectar, tiny insects, and spiders.
- The time spent in the nest by the fledglings before they are ready to leave and explore the world varies by species. It typically ranges from 18 to 30 days, during which they develop the necessary skills and strength to survive independently.
Hummingbird eggs, with their small size and unique shapes, are marvels of nature.
These delicate creations play a vital role in sustaining the hummingbird population, ensuring the survival of these tiny, vibrant creatures.
Understanding the intricacies of their eggs and the efforts put into incubation and parental care deepens our appreciation for these remarkable birds.
Remember to keep these facts in mind the next time you have the opportunity to witness the wonder of hummingbird nesting and the delicate beauty of their eggs.
Understanding The Importance Of Egg Color Research
Studying The Evolution Of Egg Colors
Egg coloration in hummingbirds has intrigued scientists for decades. By studying the evolution of egg colors, researchers gain valuable insights into the evolutionary history and behavior of these remarkable birds.
Here are some key points to understand about this fascinating field of research:
- Evolutionary significance: The color of hummingbird eggs is not merely a coincidence or random occurrence. It has evolved over time as a result of various factors, including predation, camouflage, and signaling.
- Camouflage strategies: Some hummingbird species lay eggs that blend seamlessly with their surroundings, making it harder for predators to spot them.
- Signaling behavior: In certain species, brightly colored eggs serve as a way for females to signal their genetic quality to potential mates.
- Variation across species: Hummingbird egg colors vary greatly across different species. From pale blue and green to white and even pink, each species has its own unique egg coloration.
Implications For Conservation Efforts
Understanding the significance of egg colors in hummingbirds has important implications for conservation efforts.
Here’s how this research can contribute to the conservation of these enchanting creatures:
- Indicator of habitat quality: The color of hummingbird eggs can provide valuable information about the health and quality of their habitat.
- Assessing population health: By monitoring the variation in egg colors among hummingbird populations, scientists can assess the overall health and genetic diversity of these populations.
- Conservation prioritization: The study of egg colors can aid in prioritizing conservation efforts by identifying species with unique or endangered egg coloration.
- Awareness and education: Highlighting the connection between egg colors and conservation can help raise public awareness about hummingbirds and their habitat.
How Changing Environmental Conditions Affect Egg Coloration
Environmental conditions play a crucial role in shaping the colors of hummingbird eggs.
Here’s a closer look at how changing environmental conditions can impact egg coloration:
- Impact of climate change: Rising temperatures and altered precipitation patterns associated with climate change can lead to changes in vegetation and flower availability.
- Pollutant exposure: Hummingbirds are exposed to various pollutants in their environment, including pesticides and heavy metals.
- Habitat loss and fragmentation: As hummingbird habitats shrink and become fragmented, the availability of suitable nesting sites and food sources may decline.
- Adaptation and evolutionary response: Hummingbirds have shown remarkable adaptability in the face of changing environments.
Understanding the intricacies of egg coloration research in hummingbirds sheds light on their evolutionary journey, aids conservation efforts, and unravels the impact of changing environmental conditions.
This knowledge is crucial for protecting these delicate and magnificent creatures for generations to come.
Tips For Observing Hummingbird Eggs In The Wild
Hummingbirds are fascinating creatures that captivate birdwatchers with their vibrant colors and unique behaviors. One exciting aspect of observing hummingbirds is the opportunity to witness the wonder of their nests and eggs.
Recognizing Hummingbird Nests
- Hummingbird nests are small and often well-hidden, making them a challenge to find. However, with some knowledge and observation skills, you can spot these intricate creations.
- Look for nests in trees, shrubs, and even man-made objects like clotheslines or light fixtures. These tiny structures are typically camouflaged among leaves and branches.
- Hummingbird nests are cup-shaped and constructed of soft materials such as moss, lichen, feathers, and spider silk. The outside is often covered with lichens, which helps them blend into their surroundings.
- The interior of a hummingbird nest is lined with softer materials like plant fibers, fur, or feathers, providing a comfortable space for the eggs.
- By observing the female hummingbird’s behavior, you may be able to locate their nests. They will often repeatedly visit specific plants or areas, indicating that their nest is nearby.
Ethical Guidelines For Observation
- The welfare of hummingbirds and the protection of their nests should always be a top priority when observing them in the wild. Follow these ethical guidelines to ensure responsible birdwatching:
- Keep a respectful distance from the nest to avoid causing stress or disturbance to the hummingbirds. Use binoculars or a telephoto lens to observe them from a distance.
- Never touch or handle the nest, eggs, or hatchlings. This can introduce potentially harmful bacteria or disrupt the delicate balance of the nest.
- Avoid prolonged or frequent visits to the nest site. Give the hummingbirds and their eggs the necessary space and minimize your impact on their environment.
- Refrain from sharing the exact location of active hummingbird nests publicly, as this may attract unwanted attention and increase the risk of disturbance or predation.
Resources And Tools For Birdwatchers
- As a birdwatcher, there are various resources and tools available to enhance your experience of observing hummingbird eggs in the wild. Here are a few recommendations:
- Field guides: Invest in a reliable field guide specific to hummingbirds. These guides provide detailed information on hummingbird species, their nests, and eggs.
- Online communities: Join online birdwatching communities or forums where you can connect with experienced birdwatchers, seek advice, and share your observations.
- Smartphone apps: Download birdwatching apps that offer identification assistance, bird call recordings, and other valuable tools to enhance your hummingbird observations.
- Camera equipment: Consider investing in a quality camera with a telephoto lens to capture clear and detailed images of hummingbird nests and eggs. Remember to prioritize the well-being of the birds and their environment while photographing.
Observing hummingbird eggs in the wild is a privilege that requires responsible and ethical birdwatching practices.
By following these guidelines and utilizing available resources, you can enjoy these amazing creatures while supporting their conservation efforts.
FAQ of What Color Is a Hummingbird Egg
What color is a hummingbird egg?
What size are hummingbird eggs?
How many eggs do hummingbirds typically lay?
How long does it take for a hummingbird egg to hatch?
Do male or female hummingbirds incubate their eggs?
Conclusion
The color of Hummingbird eggs is usually white or off-white with reddish-brown spots or blotches forming a speckled pattern.
This camouflaged speckled pattern helps the eggs to blend in with the surrounding environment and afford them protection from predators.
Both parents devote time to incubating and caring for the eggs until they hatch.