Why Do Hummingbirds Chase Each Other? 4 Reasons!
Hummingbirds chase each other primarily due to territorial behavior. They are fiercely territorial creatures that aggressively protect their food sources, including nectar-rich flowers and feeders, from other hummingbirds.
Hummingbirds, despite their small size, are known for being highly territorial. This behavior is largely driven by their high metabolic rates which require them to feed frequently.
As such, they’ve evolved to fiercely defend their food sources, whether it be a flowering plant or a feeder.
When another hummingbird encroaches on their territory, they will often engage in a fast-paced chase to fend off the perceived threat.
Hummingbirds are territorial animals and they defend their territories from other birds in a variety of ways.
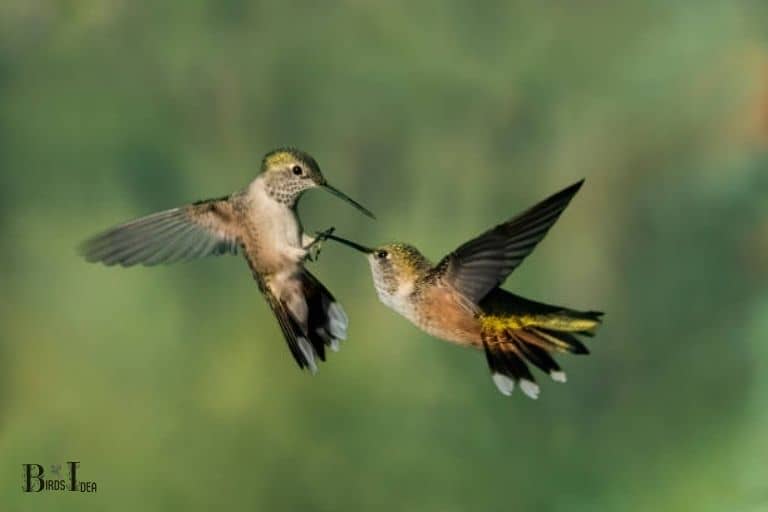
One such behavior is chasing; the male will chase another bird, either a female or a competing male, to signal that he is the owner of the area, thereby claiming the resources within it.
This way, the resources are kept safe in a defined area that nobody else can take advantage of.
4 Reasons Why Hummingbirds Chase Each Other
| Reasons Why Hummingbirds Chase Each Other | Explanation |
| Territorial Defense | Male hummingbirds are extremely territorial and will chase off other males that infringe on their space. This is to protect their food resources, which they will need for energy and to attract females. |
| Mating Rituals | During mating season, male hummingbirds will also chase females as part of their courtship display. This is done to showcase their strength and agility, which are considered desirable traits by the females. |
| Competition | Hummingbirds are highly competitive for food resources, as they need to consume a large amount of energy to sustain their high metabolism. As such, they will chase off others from a good food source, particularly if it is limited. |
| Predatory Defense | If a hummingbird perceives another bird or animal as a potential threat, it may chase it away to protect itself or its nest. |
Key Takeaway

Five Facts About: Hummingbirds Chase Each Other
DID YOU KNOW
The average hummingbird territory is between 0.3–0.9 hectares, although some can be larger, depending on the species.
Overview of Hummingbirds Territorial Behavior

Hummingbirds are known for their small size and territorial behavior. They are often seen chasing away other birds from their territory or their favorite feeder.
These territorial behaviors are likely an evolutionary adaptation to ensure that the hummingbirds have access to food and nesting sites.
Hummingbirds use a variety of behaviors to establish their territory. They may perform aggressive displays such as chasing away other birds, making loud noises, or displaying bright colors.
They may also claim a specific territory by flitting around its edges and guarding it from intruders.
In addition to territorial behavior, hummingbirds also use a variety of vocalizations to communicate with one another.
These vocalizations may be used to let other hummingbirds know they are in an area or to indicate they are defending a territory.
It is important to note that territorial behavior is a natural part of the hummingbird’s behavior and should not be discouraged.
However, if the behavior becomes overly aggressive or destructive, it should be discouraged in order to prevent harm to the hummingbirds or other wildlife.
The Significance of Territorial Behavior in Hummingbirds

Territorial behavior is an important part of hummingbird ecology, as it is a key factor in the competition for resources such as food and mates.
Territoriality among hummingbirds involves a variety of behaviors, including singing, flying, and attacking. In order to maintain their territories, hummingbirds must be able to distinguish their own territory from the territory of their rivals.
Territorial behavior is important in the regulation of food resources. By defending their territories, hummingbirds are able to ensure that they have access to the food that is available in their area.
As a result, territorial behavior can have a significant impact on a hummingbird’s reproductive success.
In addition to food resources, territorial behavior also plays an important role in the competition for mates. Male hummingbirds often display territorial behavior in order to attract females and to keep out rival males.
Male hummingbirds use a variety of tactics to defend their territories, including chasing, vocalizing, and attacking.
Overall, territorial behavior is an important factor in the ecology of hummingbirds, as it helps them to regulate food resources and to compete for mates.
Territoriality plays a key role in the survival and reproductive success of hummingbirds, and it is essential to understand its importance in order to protect these birds and their habitats.
How Hummingbirds Establish Boundaries by Chasing?

Hummingbirds are well known for their colorful plumage and impressive aerial skills. However, these small birds also use their aerial acrobatics to establish territorial boundaries and protect their food sources.
Hummingbirds do this by chasing away intruders in their territory.
When a hummingbird notices an intruder entering its territory, it will fly directly towards the intruder and will often also make a loud, high-pitched noise. If the intruder does not leave the area, the hummingbird will repeatedly chase it until it flies away.
This is the hummingbird’s way of establishing its boundaries and protecting its food sources.
Hummingbirds are also very resourceful birds when it comes to defending their territories. They will often perch in higher places such as tree branches or powerlines and survey the area.
If they see an intruder coming, they will quickly fly down and chase it away. This behavior is most commonly seen during the breeding season when males will fiercely defend their nesting territories from other males and females.
Hummingbirds rely on their territorial boundaries in order to find and secure the necessary resources for survival. Without the ability to establish and defend their boundaries, hummingbirds face the threat of competition from other birds or animals.
As such, it is important for hummingbirds to establish their boundaries and protect their food sources through chasing.
What Resources Do Hummingbirds Claim When They Chase?

Hummingbirds are important to the environment due to the pollination of plants and flowers that they help provide. When a hummingbird is searching for nectar, they will often chase away other birds from their chosen location.
In order to do this, they claim certain resources in their environment that other birds may be trying to use.
The main resources that hummingbirds will claim when they chase include:
Food Sources: Hummingbirds will claim food sources like flowers and nectar. They will also claim insects that they can find in their environment.
Territory: Hummingbirds will also claim certain patches of their environment as their own. This includes areas of air space that they will defend from other birds and animals.
Mating Rights: When two hummingbirds are competing for the same mate, they may claim mating rights to that particular individual. This will involve a lot of chasing and can create a lot of noise and activity.
In addition to these resources, hummingbirds may also claim areas of vegetation and trees in order to build their nests. This can be a very territorial process and other birds may be chased away from their nesting grounds.
Overall, hummingbirds will claim a lot of resources when they chase. This can include food sources, territory, mating rights, and areas of vegetation in order to build their nests.
By claiming these resources, they can ensure they have enough to sustain themselves and the environment.
What Effects Does Territorial Behavior Have on Hummingbirds?

Territorial behavior plays an important role in the lives of hummingbirds, as it helps them to establish their own space and resources to survive.
Territorial behavior in hummingbirds typically involves the males aggressively defending their space from other male hummingbirds, while also attracting mates.
Generally, a male hummingbird will stake out a certain territory, which often includes a food source, and then defend it from other hummingbirds.
There are a number of effects that territorial behavior has on hummingbirds:
- First, it allows them to establish their own home ranges and sources of food, which can be beneficial for their survival.
- Second, territorial behavior allows them to protect themselves from predators.
- Third, it helps them to attract mates, as the more dominant males will have the best territories and therefore be the most attractive mates.
- Finally, territorial behavior can reduce competition for food and resources, as other hummingbirds may be less likely to come into their territory if they encounter aggression.
For example, a male hummingbird may establish a territory around a feeder, aggressively defending it from other male hummingbirds. This will allow the male to have access to the feeder without having to compete with other hummingbirds.
At the same time, he may be more attractive to potential mates due to his dominance in the area.
Are There Any Strategies Used by Hummingbirds to Defend Their Territories?

Hummingbirds are known for their territorial nature and use various strategies to defend their territories from other hummingbirds.
Some of the strategies used by hummingbirds to defend their territories include:
1. Visual displays: Hummingbirds will perform aerial displays and dive-bombing to show potential intruders that the territory is occupied.
2. Vocalizations: Hummingbirds will make a variety of vocalizations to show other hummingbirds that the territory is taken.
3. Physical aggression: Hummingbirds will chase away or even fight other hummingbirds that intrude on their territory.
4. Nest defense: Hummingbirds will fiercely guard their nests and will use aggressive behavior to keep other hummingbirds away.
These strategies are used by hummingbirds to protect their resources, such as food sources and nesting sites, from other hummingbirds.
For example, a male hummingbird may circle its territory and perform aerial displays to try and keep other hummingbirds away from its food source.
What Are the Other Ways of Signaling Ownership Among Hummingbirds?
Among hummingbirds, signaling ownership is usually done through territorial displays and aggressive calls. Other methods include body posturing, wing flashing, head-bobbing, and tail-spreading.
Territorial displays are likely the most common way for hummingbirds to signal ownership. These displays involve a hummingbird rapidly flapping its wings, chasing and dive-bombing intruders, and making loud calls to warn them off.
Body posturing is also used to signal ownership, with a hummingbird often puffing out its throat feathers and raising its crest.
Head-bobbing is a less common way of signaling ownership, with a hummingbird bobbing its head back and forth as a warning to potential intruders.
Tail-spreading is another way of signaling ownership, with a hummingbird often displaying its colorful tail feathers to ward off intruders. By combining all of these behaviors, hummingbirds can effectively signal their ownership and deter intruders from entering their territory.
As an example, a female Ruby-throated Hummingbird may rapidly flap its wings, puff out its throat feathers, bob its head, and spread its tail feathers to convey ownership to a potential intruder.
This display is usually enough to keep an intruder at bay and protect the hummingbird’s territory.
“The most courageous act is still to think for yourself. Aloud.”
-Coco Chanel
FAQ of Why Do Hummingbirds Chase Each Other
Why do hummingbirds chase each other?
How fast can a hummingbird fly?
Is it true that hummingbirds eat constantly?
Do hummingbirds migrate?
Is it okay to feed hummingbirds during cold weather?
Conclusion
Male hummingbirds chase other hummingbirds in order to establish a territory and claim resources within it.
This behavior serves as a signal of ownership and helps them to determine the boundaries of their territory.
Having an established home range keeps resources secure and allows the birds to thrive in their environment.